[Gaze Estimation] Vision-based Gaze Estimation: A Review (1)
‘Vision-based Gaze Estimation-A-Review’ review

0. Abstract
-
Gaze estimation은 head pose, optical axis, visual axis, eye blink, occlusion, image blur에 취약하다.
-
본 논문은 위 문제점들을 다룬 논문들을 소개하고, gaze estimation의 future direction 및 challenges를 제시한다.
1. Introduction
-
Gaze estimation은 human behaviors 분석에 필수적이기 때문에, gaze direction을 estimate 하는 것은 human-centered science 및 technology에 중요하다.
-
Gaze estimation 수행을 위해서는 아래와 같은 문제점들이 있다.
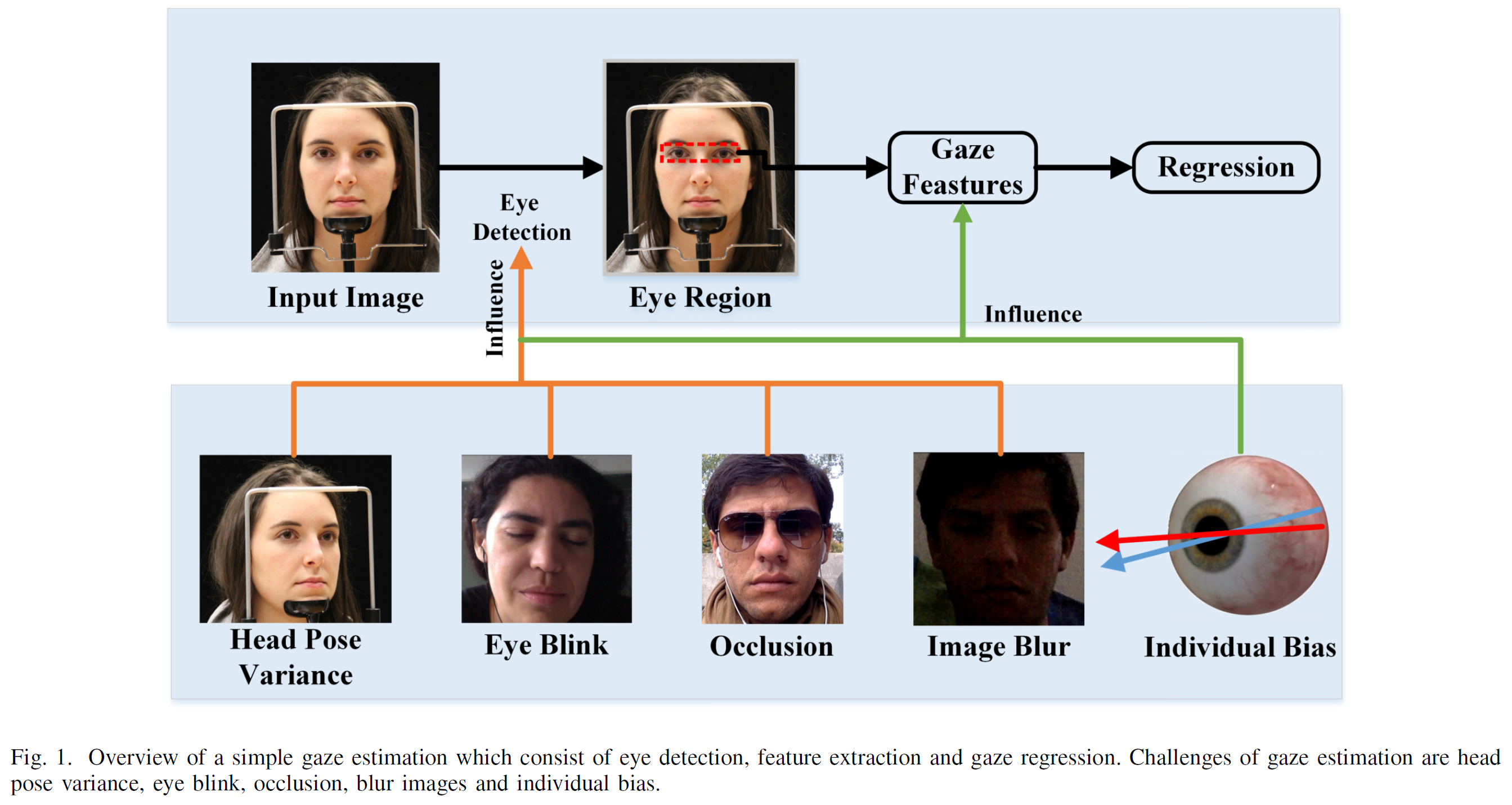
-
fig. 1은 Gaze estimation의 normal process 및 challenges를 나타낸다.
-
상기 문제점들을 해결하지 않고는 regressor가 제대로 gaze를 estimation하는 것을 기대하기는 힘들다.
-
지난 Review 논문과는 다르게 본 논문에서는 gaze estimation에 관한 existing challenges와 solution에 관해서 다룬다.
-
Contribution은 아래와 같다.
-
Gaze estimation에 관한 existing challenges - solutions, datasets, applications에 관한 정리
-
Gaze estimation에 관한 future possible prediction.
-
-
Section 소개
-
Main challenges and ideas for solving challenges
-
Datasets
-
applications
-
future direction
-
2. Challenges and solutions
-
2.1. Head pose variance
-
Visual gaze의 70% 정도는 head pose로 부터 나오는 것이기 때문에, gaze estimation에 있어서 head pose는 매우 중요하다.
-
따라서 Head pose로 robust한 gaze를 측정하고, eye-region으로부터 grained gaze를 extract 해내는 방식을 사용한다.
-
또한 head pose는 eye region shape을 변형시켜, gaze estimation에 또 다른 영향을 준다. (fig. 2 참조)
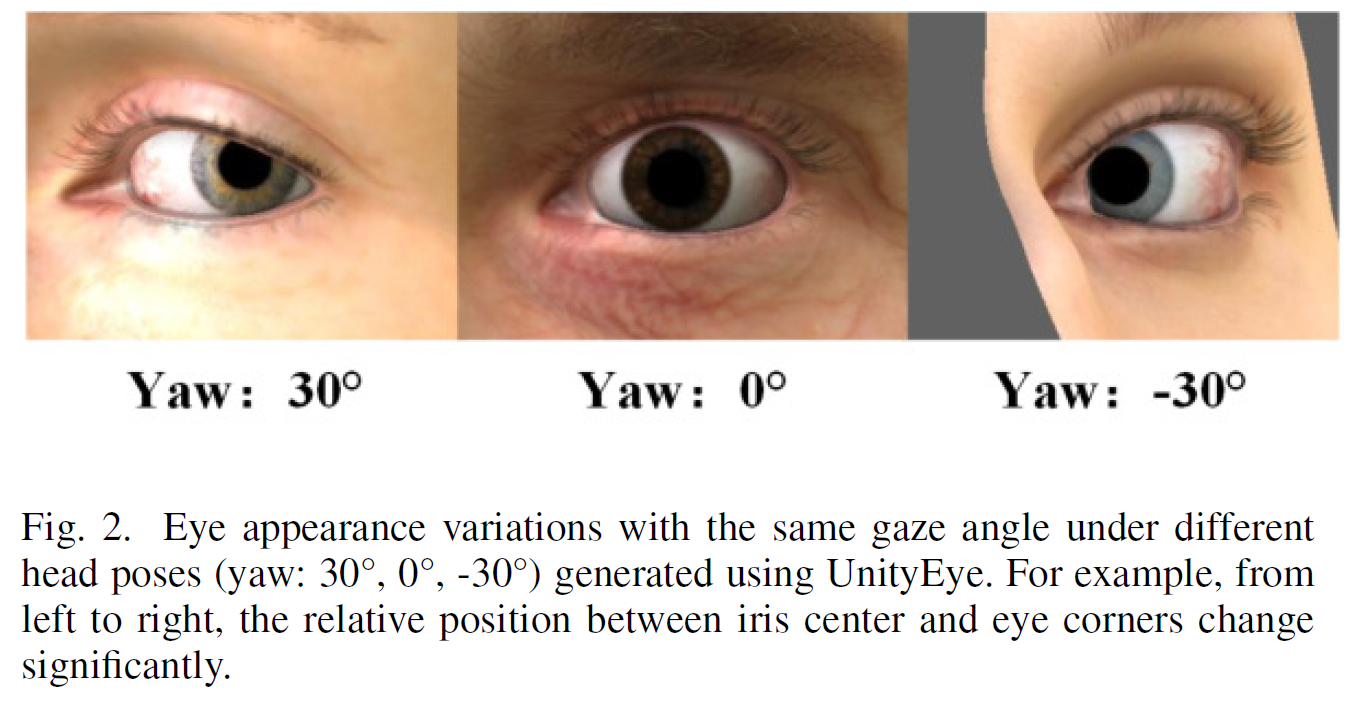
-
즉, head-pose invariant한 feature based가 아니면, head pose에 따라서 Gaze가 크게 영향을 받을 수 있다는 것이다.
-
주목할만한 observation 중 하나는, object가 사람 바로 앞에 있을 때보다, object가 사람의 오른편에 있을 때 head pose와 gaze 사이의 offset이 더 크다는 사실이다.
-
아래에서 Head pose에 관한 Gaze의 dependency를 낮출 수 있는 방법들을 소개한다.
-
2.1.1. Cluster-based method
-
첫 번째 방법은 head pose의 cluster를 만들고, cluster마다 gaze estimation model을 만드는 것이다.
-
[5]에서는 multiple camera를 사용해서, 각 모델의 random forest로 eye region으로부터 gaze를 판정하는 방법을 사용했다. (Error 6.5 in UT-Multiview dataset)
-
[7]에서는 CNN based method를 사용했다. (5.65, 5.3 error in columbia dataset and MPIIGaze dataset)
-
-
2.1.2. Face frontalization-based method
-
두 번째 방법은 Head의 3D-Model을 기반으로 head pose를 eliminate해서 강제로 frontal face image로 만든 후, gaze estimation을 수행하는 방식을 뜻한다.
-
[8]에서는 face와 3D Mesh data를 찾고, key point를 extraction해서 symmetry place을 만듬으로써 virtual frontal face image를 rendering한다.
-
그 후 eye를 3D Eye model에 mapping 시켜서 gaze를 estimation한다.
-
[12]에서는 face의 dense markers를 기반으로 cascade regression을 수행해서 2D에서 3D로 변환시킨다. 그 후 Eye landmark를 이용해서 SVM(Support Vector Machine)을 사용해서 regression task를 수행한다.
-
-
2.1.3. Feature fusion-based method
-
Feature fusion은 multi-model feature를 사용해서 classification 및 regression accuracy를 향상시키는 방법이다.
-
[13, 14]는 kinect를 사용해서 head pose를 estimate하고 eye region의 capture로부터 iris displacement vectors 및 reference points를 추출하여 head position 및 head pose와 함께 Bayesian multinomial logistic regression의 input으로 사용하여 gaze estimation을 수행했다.
-
[15]는 crop한 eye region을 LaNet의 input으로 넣어서 gaze estimation을 수행했다. (6.3 error in MPIIGaze dataset)
-
[18]은 LaNet 대신에 VGG를 사용해서 MSE를 5.5까지 향상시켰다.
-
그 이후에도 네트워크 구조를 늘리거나, GAN을 사용해서 Image를 refine 한 후 estimation 하는 방식을 통해서 accuracy를 향상시켰다.
-
-
2.1.4. Geometric Relationship-Based Method
-
Geometric relationship based method는 안구 모델의 기하학적인 성질과 head movements를 compensate 할 수 있는 transformation을 활용한 방식을 의미한다.
-
Head pose와 eye는 총 6개의 DOF (Degree of Freedom)을 가지며, 그 중 4개 (Translation x, y, z-axis, rotation z-axis)를 공유한다.
-
[5]는 camera를 eye center와 맞게 align 시켜, 두 개의 DOF (Pitch, Yaw) 만 남긴다. 또한 focal-length를 조절해서 image의 size를 거의 같게 조절한 후에 Gaze를 estimation 하여 error를 줄였다.
-
대부분의 SOTA 논문들은 이 방식을 사용하였다.
-
-
2.1.5. Auto-Encoding-Based Method
-
Auto-encoding based method는 head pose information과 gaze information을 learning based method로 encoding 하는 것이다.
-
[28]은 Spatial attention module을 사용해서 eye region에 weight를 줘서 관련 없는 부분을 솎아내고, head pose information과 gaze information을 함께 encoding하여 gaze를 estimation 하였다. (4.8, 6 error in MPIIFACEGaze, EYEDIAP datasets)
-
[29]는 gaze estimator, appearance classifier, head pose classifier에 fed시키고, adversarial learning method를 사용하여 한번에 head pose 및 gaze representation method를 learning 시키는 방법을 사용했다. (4.3, 5.4, 9.9 error in the MPIIGAZE, UT-Multiview, EYEDIAP datasets)
-
[30]은 head pose 및 gaze를 simultaneously하게 detect하는 multi-task method를 사용했다.
-
이러한 End-to-End method는 face 및 eye를 multi-stream CNN으로 추출하고, head pose 및 gaze direction을 parallel architecture로 learning을 진행한다. (error 0.82, 4.02 in the columbiaGaze and MPIIGaze)
-
-
-
2.2 Person-Specific Bias
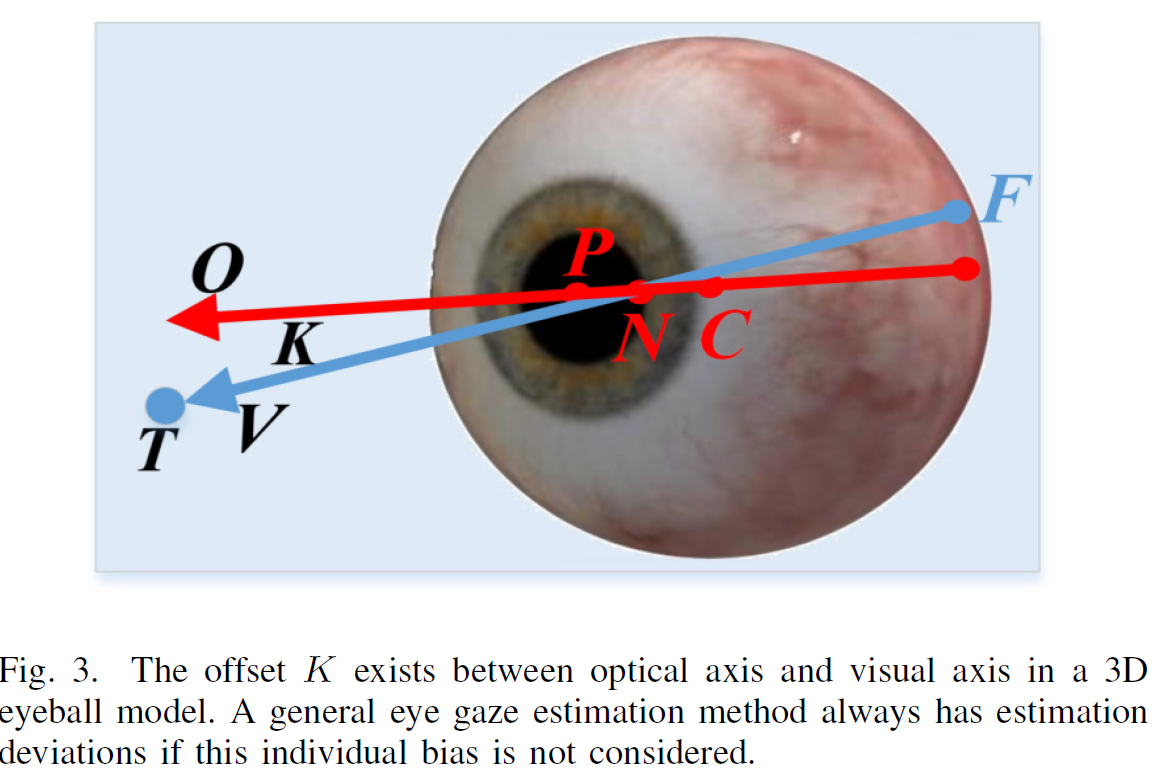
-
[38]에서는 person-specific bias를 optical axis와 visual axis의 차이로 나타냈다. 여기서 optical axis란 fig. 3의 빨간 선으로써, eye-ball의 center $C$와 pupil의 center $P$를 잇는 빨간 선을 의미한다. Visual axis란 fovea와 Target을 잇는 파란 선을 의미한다.
-
이 때, Visual axis는 $V$, Optical axis는 $O$, person-specific offset은 $K$로 나타낸다.
-
이러한 person-specific bias 교정 없이 gaze estimation을 하면, 이는 error를 유발할 수 있다고 했고, 이번 section에서는 이를 다룬 논문들에 관해서 알아본다.
-
2.2.1. Parameters Estimation-Based Method
-
[34, 35]는 두 카메라와 두 광원을 사용하고, 두 안구의 visual axis가 항상 intersect한다는 가정 하에서, 두 안구의 gaze point를 optimization 시켜서 K를 도출해 내는 방식을 사용했다.
-
[36]은 active calibration 없이, quadratic programming을 이용해서 inequality-constrained optimization problem을 solve하는 방식을 사용했다.
-
[40]은 gaze representation시, person specific calibration parameters를 추정하기 위해서, full face image와 calibration parameters를 input으로 CNN Network를 사용하여, 결과적으로는 적은 수의 calibration sample만 가지고도 정확도 높은 calibration을 가능하게하고 그 후 gaze estimation을 수행한다.(error 2.7 MPIIGaze dataset)
-
-

댓글남기기