[Image recognition] Grounded Language-Image Pre-training
Grounded Language Image pre-training review

0. Abstract
-
object-level, language aware, semantic-rich visual representations을 위해 object detection - phrase grounding unified network은 GLIP (Grounded language-image pre-training) model을 제안
-
제안하는 모델은 Detection 및 grounding accuracy를 둘 다 향상 가능하고, self-training 방식을 위해 massive한 image-text pair data를 leverage 할 수 있다.
-
27M grounding data (3M Human annotated), 24M web-crawled image-text pair data로 훈련하여, COCO 및 LVIS Datasets에서 49.8AP, 26.9AP를 달성했다.
-
COCO Training data로 훈련 후에는 60.8 AP, 61.5 AP를 달성했다.
-
Object detection에 관한 13개의 task 에서, 1-shot transfer learning으로 fully-supervised dynamic head와 비슷한 결과를 냈다.
-
Idea) Image-text pair로 훈련시킨게 왜 각 task에서 더 성능이 좋지? 두 task 간에 필요로 하는 weight는 서로 다를텐데, 어떻게 상호보완적인 결과가 되는걸까?
1. Introduction
-
Visual recognition의 기존 model들은 pre-determined sample 위주로 학습하여 generalization 성능이 떨어진다.
-
CLIP은 image-text pair data가 image-level visual representation을 학습하는데 좋다는 것을, 학습 후 image classification 혹은 text-image retrieval task에 transfer learning한 결과가 좋다는 것을 보여줌으로써 입증하였다. 하지만 fine-grained feature가 필요로 되는 task (object detection, segmentation ..)에는 부족함이 있었다.
-
본 논문에서는 Phrase grounding이 object-level, language-aware, semantic-rich visual representation task에 transfer-learning시에 효과적임을 입증하고자 한다.
-
Parase grounding: Object - sentence간의 fine-grained correspondence를 확인하는 작업을 의미
-
제안하는 방법은 object detection 및 phrase grounding을 통합함으로써, object detection을 context-free phrase grounding (즉, 이미지 전체의 맥락 보다는 각 객체에 집중한 phrase grounding) 으로, phrase grounding을 contextualized object detection task (각 object의 phrase로 전체 context를 추론하는 task) 로 보는 방법이다.
-
1.1 Contribution
- Unifying detection and grounding by reformulating object detection as phrase grounding
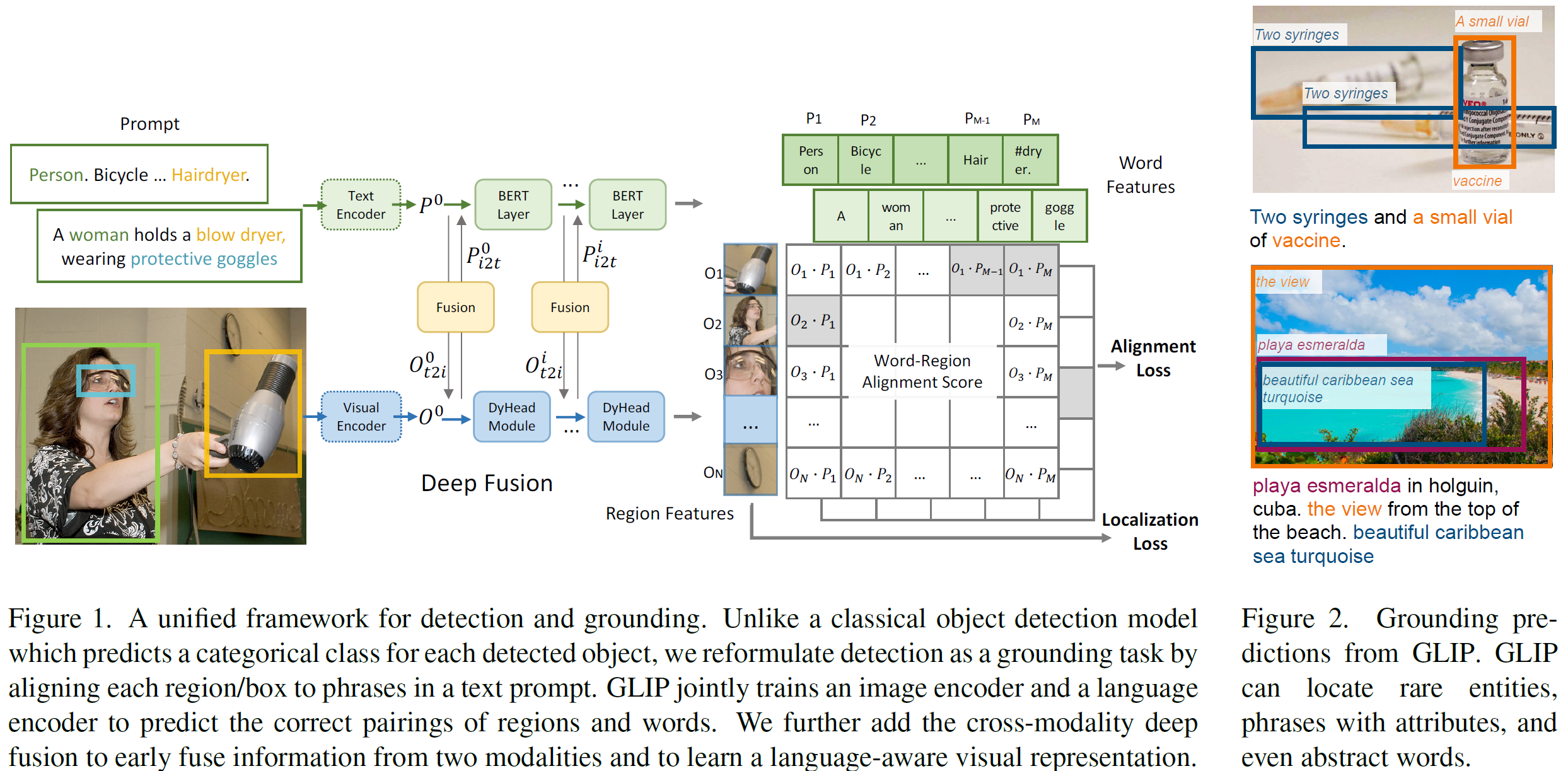
-
Detection model의 input을 일반 image에서, 일반 image + image description sentence로 변경하는 방법을 사용했다.
-
또한 dual-encoder 형식을 취하여 두 feature을 곱하는 방식으로 하나의 feature로 통합시키고자 하였으며, 이 방식을 통해 모든 object detection model에 본 방식을 적용 가능하게했다.
-
CLIP은 마지막에 dot product layer를 통해서 두 특징을 고려하는 반면에, 본 architecture에서는 deep fusion 방식을 사용했다.
-
결과적으로 볼 때, detection 및 grounding side 모두 성능이 향상되었다.
- Scaling up visual concepts with massive image-text data
-
GLIP 학습을 위해, 27M grounding data(human-annotated fine-grained data (3M) + web crawled data (24M))에 NLP parse를 teacher model로 삼고 pseudo annotations을 진행하여 data를 refine했다.
-
figure 2에서 확인 가능한 것처럼, 본 방식을 통하면 pre-determined label이 아닌 경우에도 prediction이 가능해 LVIS 및 13개의 down=stream task에 관해서 큰 성능 향상을 이끌어 냈다.
-
COCO 2017 val, test에서는 60.8 AP 및 61.5 AP를 이루어냈다.
- Transfer learning wigh GLIP: one model for all
-
앞선 두 contribution인, grounding reformulation 및 semantic-rich pre-training을 통해 human annotations 없이도 COCO 및 LVIS에서 좋은 성능을 이끌어냈고, 13개의 object detection 관련 task에서도 좋은 결과를 이끌어냈다.
-
또한 Object 365를 통해 10-shot supervised baseline보다 GLIP-L로 1-shot training 한 결과가 비슷한 수치가 도출되었다. (1-shot? class 중 하나가 겹친다는 말인가? 보통 stage의 개념이 shot 아닌가?)
-
또한 GLIP 모델 전체가 아닌, 특정 기능을 수행하는 부분만 부분적으로 fine-tuning 한 경우에도 결과가 뛰어났다.
2. Related work
-
기존 object detection을 훈련시키기 위한 데이터 셋들을 크게 만드는데는 많은 비용이 든다.
-
GLIP는 Phrase grounding을 object detection과 접목시켜서 image-text의 massive한 paired data를 활용하여 이를 극복하고자 했다. (이 방법이 해결 방안이 될 수 있는 이유는 크롤링을 적용해서, bounding box 없이도 detector를 훈련시킬 수 있게 한다는건가?)
-
GLIP는 Dynamic Head 기반으로 구현되어 있으며, 어떤 object detector에도 부착 가능하다.
-
최근에는 visual representation problem을 풀기 위해, language supervision 없이 (?) vision -language 방식을 사용하는 CLIP, ALIGN 모델 등이 Contrastive learning 방식을 이용해서 open-vocabulary image classification을 수행했다.
-
또한 MDETR은 End-to-End 방식으로 image-text matching problem을 해결했다.
-
본 논문은 transfer-learning에 집중하고 있고, various task, domain에 적용할 수 있기를 바라지만, zero-shot은 아니다. 이는 우리가 데이터 셋으로부터 rare한 category라도 배제하지 않았기 때문이고, 그 이유는 rare한 sample이 가지는 information이 rich해서 rare한 category prediction에 도움을 줄 것으로 예상되기 때문이다
-
이런 방식은 open-vocabulary object detection과 유사하지만, 그와 다르게 우리는 실제 transfer-learning 시 고려되어야하는 cost에 더 집중했다.
3. Grounded Language Image Pre-training
-
Object detection과 phrase grounding은 image 내 object에서 semantic concept을 도출한다는데 공통점이 있고, 이 점에 착안해서 본 모델을 구성했다.
-
3.1. Unified formulation
-
3.1.1. Background: object detection
-
전형적인 object detector는 input으로 image를 받고, backbone network를 통해 feature extraction을 수행하고 그 후, box classifier와 bounding box regressor를 사용해서 prediction을 진행한다.
-
학습에 사용되는 loss는 classification loss $L_{cls}$, localization loss $L_{loc}$로 나뉘며 통합된 loss는 아래 식과 같다.
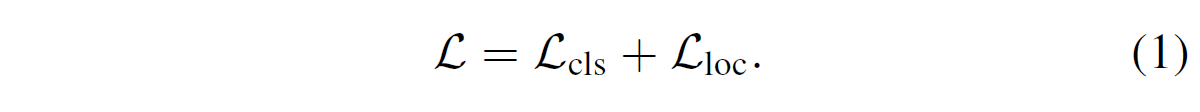
-
Two stage detector에서는 region proposal network (RPN)을 이용해서 sample의 background, foreground 여부를 판정하고 최종 anchor를 refine 하는데, 이 때 class에 관한 정보가 사용되지 않으므로 본 논문에서는 localization loss인 $L_{loc}$에 RPN loss를 통합했다.
-
또한 one-stage detector에서는 $L_{loc}$에서 centerness가 사용되기도 한다.
-
뜬금없이 이 내용이 왜 나오는거지? 본 논문에서 사용한건가? 그리고 anchor-based 방식에서 centerness를 사용하나?
-
Classifier는 단순한 linear layer로 구성되고, classification loss $L_{cls}$는 아래와 같이 나타낼 수 있다.
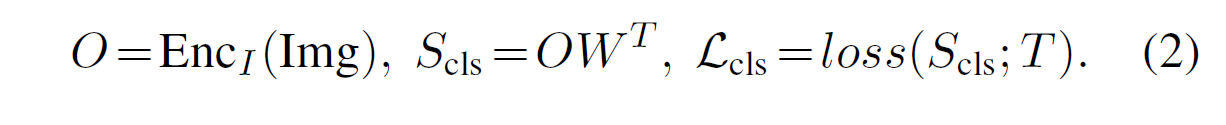
-
$O \in R^{NxD}$: Input image -> backbone network의 output
-
$W \in R^{CxD}$: Weight matrix for box classifier
-
$S_{cls} \in R^{Nxc}$: output classification logits
-
$T \in 0^{Nxc}$: target
-
loss: Two stage에서는 cross-entropy, one stage에서는 focal loss.
-
-
3.1.2. Object detection as phrase grounding
-
3.1.2.1. object - phrase classification standard
-
각 proposal을 c개의 class로 분류하는 대신에, 본 논문에서는 c개의 phrase로 분류하는 방법을 사용한다.
-
c개의 phrase로 분류하는 가장 간단한 방법은 class name을 그대로 사용하는 것이다. (i.e. Prompt = “detect: person, bicycle, car, …, toothbrush”)
-
본 논문에서는 Pre-trained BERT를 사용해서, “person, bicycle, car, toothbrush”처럼 명사 단위로 분류 가능하도록 encoder $EnC_L$을 Initialize 했고, 이 결과가 좀 더 human-friendly한 phrase를 사용하는 것 보다 결과가 더 좋았다. (Section 5.2 참조)
-
-
3.1.2.2. Grounding model
- Grounding model은 image encoder $Enc_I$ 및 language encoder $Enc_L$로 구성되며, 각 encoder의 output간의 correlation은 alignment score를 통해 계산된다.
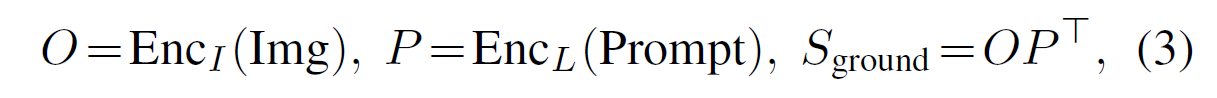
-
Notation: O = Image encoding output, P=Prompt encoding output, $S_ground$ = alignment score
-
즉, 이 구조는 일반적인 detector에서 backbone에서 나온 output이 classifier에 해당하는 weight (P) 를 통해 loss ($S_ground$)가 도출되는 과정과 흡사하게 되어있다고 생각하면 된다.
-
도출된 $S_{ground} \in R^{NM}$ 과 target matching시에 phrase중 중요한 부분을 positive matching 시키고, added-token을 negative matching 시키기 위해서, $R^{Nc} \to R^{N*M}$로 label을 변형하고, phrase내에 속한 token의 probability의 average로 phrase의 probability를 결정지었다.
-
또한 loss는 multi-label cross-entropy를 사용해서 multi-label로 token마다 loss를 구한 후 average하는 방식으로 사용하였다. (Section 4, 5 확인 필요!)
-
-
3.1.3. Equivalence between detection and grounding
-
소개했던 reformulation을 이용해서 우리는 어떤 detection model도 전부 grounding model으로 변환할 수 있다.
-
또한 Dynamic head object detector에 reformulation을 적용하기 전과 후의 evaluation 결과가 같다는 점에서, 우리는 이론적으로는 detection과 grounding의 training 및 inference 과정이 같다는 것을 확인할 수 있었다고 한다.
-
이러한 점들은 GLIP model이 zero-shot manner로 arbitrary detection task를 가능하게한다.
-
-
3.1.4. Related work
-
제안하는 grounding formulation 방식은 MDETR과 매우 유사하고 loss 역시 MDETR의 contrastive loss와 유사하지만, reformulation 및 simple unified loss로 더욱 좋은 결과를 얻었다.
-
또한 proposed grounding model은 여러 zero-shot detection model들과 유사하지만, GLIP는 detection과 grounding을 통합하는 방식을 사용한다는 점이 다르다. (zero-shot detection에 관한 조사 및 GLIP와의 명백한 차이점 조사가 필요)
-
-
-
3.2. Language-Aware Deep Fusion
-
Equation 3에서는 image와 text가 alignment score를 계산하기 위해서 최종단에서만 곱해지는 것으로 나와있지만 (late-fusion 방식), vision-language literature에서는 visual - language간의 deep fusion 방식을 필요로 한다.
-
그러므로 우리는 image 및 text encoding layer 간의 deep fusion을 수행하는 방식을 사용한다.
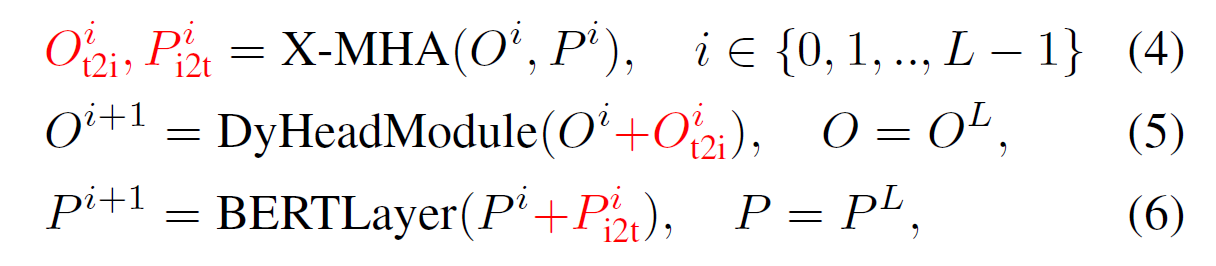
-
Notation: $O^{0}$: Output of vision backbone, $P^{0}$: Output of language backbone (BERT), L: The number of Dynamic modules, X-MHA: cross-modality multi-head attention.
-
즉, 각 backbone의 output을 받아서, Dynamic module 및 BERT Layer (Pre-trained BERT’s top layer)를 거치면서 각 output을 multi-head attention으로 묶는 방식을 통해, 기존 output + fused output을 다음 레이어의 input으로 받는 과정을 되풀이하며 진행한다.
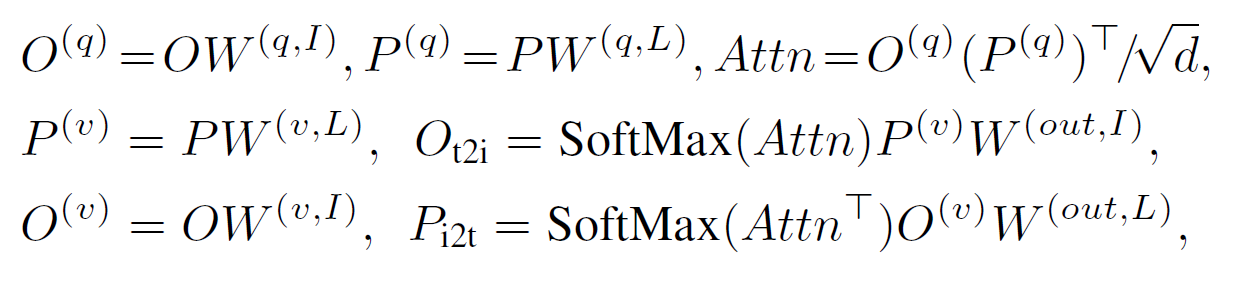
-
위 식은 일반 transformer와는 다르게 , query, value, output으로 구성되어 있다. 개인적으로는 image와 language사이의 attention을 찾는 것 이기 때문에, image와 language vector가 서로서로 query, key의 역할을 하기 때문에 따로 key라고 하는건지..? (내용 추가 필요)
-
결론적으로, deep-fused encoder는 두 가지 이점을 가진다.
-
Phrase grounding performance를 향상시킨다.
-
Visual feature이 language feature를 배울 수 있게 해서, prediction이 text prompt의 영향을 받게 하여, 다양한 downstream detection task를 잘 수행할 수 있게 한다.
-
-
-
3.3. Pre-training with Scalable Semantic-Rich Data
-
Human annotation은 너무 costy했기 때문에, 기존에는 teacher detector로 psuedo label을 만들어서 학습하는 방식을 사용하곤 했지만, 그 방식은 기존 데이터셋에 있는 카테고리만 학습 가능한 단점이 있었다. (최대 2000개 가량의 카테고리)
-
반면에 제안하는 방법을 사용했을 때, grounding data + detected data로 구성한 self-training 방식을 사용하여 좀 더 data가 담고있는 정보의 양을 semantic하게 늘릴 수 있었다. (Flickr30K - 44,518, VG Caption - 110,689)
-
또한 우리는 human_annotated data (detection + grounding)를 사용해서 GLIP를 훈련시켜 teacher model로 삼아 image-text data를 추출하고, NLP Parser를 이용해서 noun phrase를 추출한 후, student model을 훈련시켜서, figure 2에서 확인했던 것 처럼 좋은 결과를 이끌어냈다.
-
왜 student model이 teacher model보다 좋을까? 그 이유는 teacher model은 noun phrase가 포함되지 않은 데이터셋으로 학습했기 때문에, 즉 rich-language context 없이 훈련했기 때문에, 배우지 않은 카테고리에 관해 결과를 도출해낼 수 없기 때문이다. 저자의 말에 따르면 “Educated guess”를 하지 못하는 것이다.
-
4. Transfer to Established Benchmarks
-
GLIP의 성능을 보여주기 위해 활용한 데이터 셋은, MS-COCO (Object detection), LVIS (Object segmentation with 1000 categories), FLickr30K (Phrase grounding) Datasets 총 3가지다.
-
또한 ablation study처럼 3가지의 핵심적인 기능에 관하여 검증을 진행하였는데, Table 2는 검증 시 configuration을 의미한다.
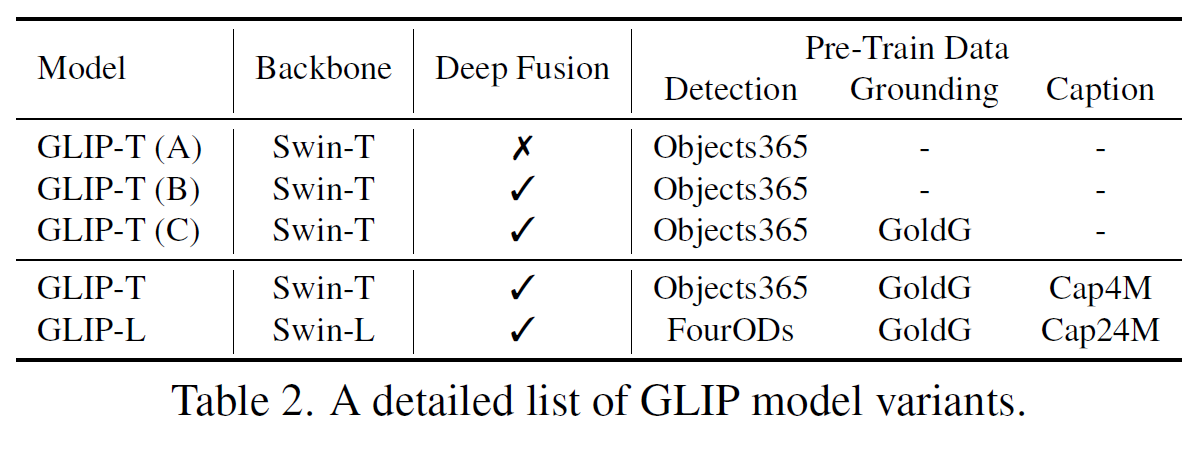
-
GLIP-T (A)
-
Dynamic head based model.
-
Classification loss -> word-region alignment loss
-
Language encoder를 사용한 것으로 볼 때, lately fusion 방식을 사용한 것으로 추정
-
Object 365 dataset으로 pre-training
-
Backbone은 Swin-tiny
-
-
GLIP-T (B)
- A에서 Deep fusion 방식을 추가
-
GLIP-T (C)
-
COCO Dataset을 활용하지 않음
-
Gold grounding ata (human annotated data)를 활용 (Flickr30K, VG Caption, GQA)
-
-
GLIP-T
-
Data set: GLIP-T (C)에서 활용한 데이터 셋 + Object 365 + Cap4M (Web + GLIP-T (C)로 Pseudo labeling)
-
CC (Conceptual Captions with 3M Data) + SBU Dataset을 추가적으로 사용하니 성능이 조금 더 향상됨.
-
-
GLIP-L
-
Backbone: Swin-Large model
-
FourODs + Object 365 + OpenImages + Visual Genome + IMageNetBoxes + Gold ground (GLIP-T (C)) + CC12M + SBU + 24M with generated boxes (NLP Parser model)
-
-
4.1. Zero-shot and Supervised Transfer on COCO
-
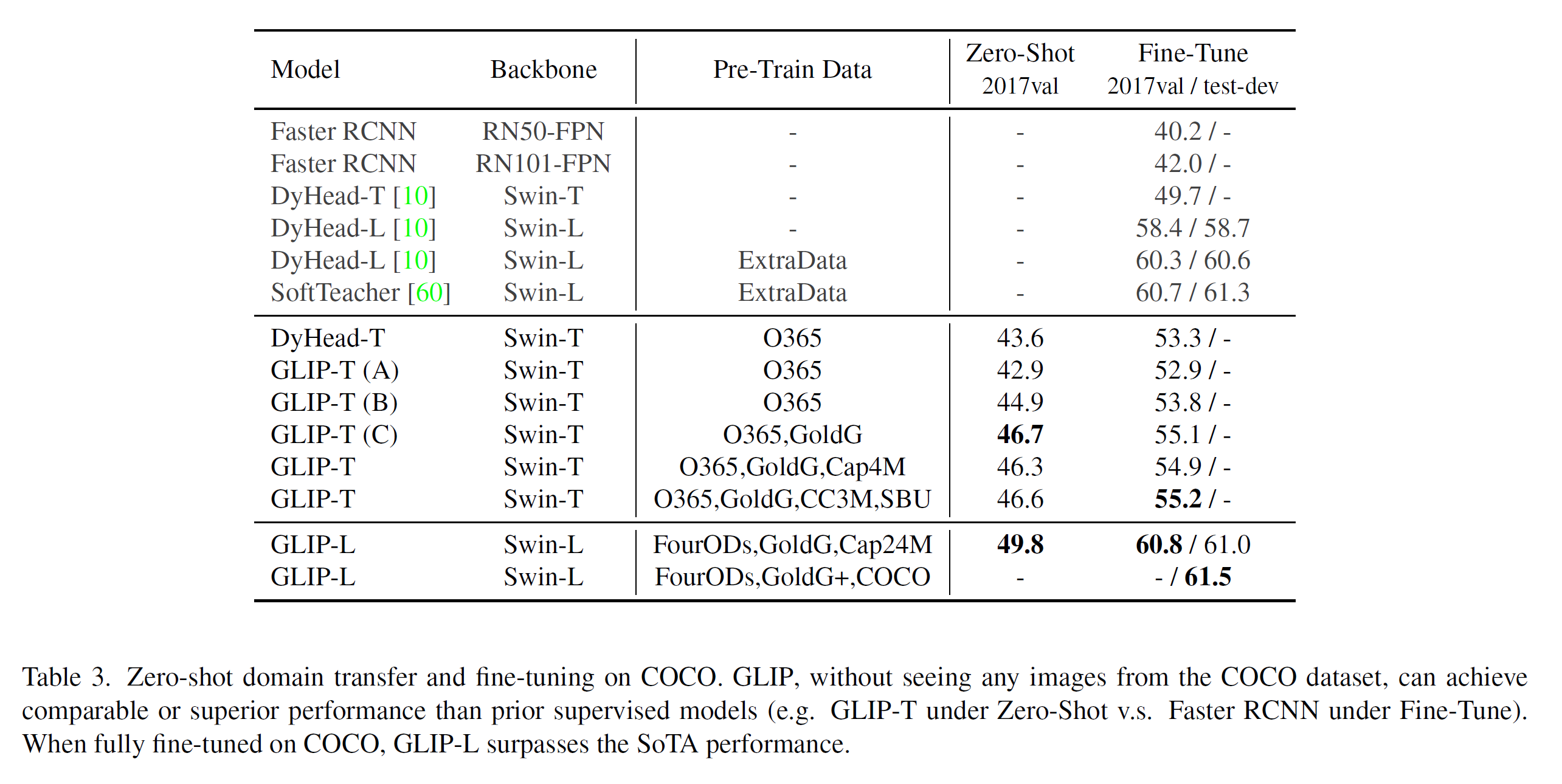
GLIP의 Transfer ability를 검증하기 위해서 COCO Dataset을 활용하여, 조건을 zero-shot transfer 및 fine-tune transfer로 나누어 실험을 진행했다.
-
추가적으로 GLIP-L Model의 fine-tuning 결과 역시 검증하였다.
-
또한 Dynamic Head model을 Object 365 dataset으로 훈련시키고, COCO Dataset에 대해서 zero-shot evaluation을 진행했다. (COCO의 모든 Categories는 Object 365에 포함되어 있다.)
-
결과는 Zero-shot GLIP Model이 supervised model보다 성능이 더 좋았다. (특정 모델에 비해서는)
-
특히, Fine-tuned GLIP-L model은 COCO에서 60.8 AP, 61.5 AP를 2017 val, 2017 test set에서 다른 bells (EMA, Mix up, label smoothing… ) 없이 달성했다.
-
이와 같은 결과는 COCO에 모든 Categories를 Object 365가 가지고 있고, deep fusion 방식을 사용했고, 마지막으로 grounding data를 사용했기 때문이라고 언급하고 있다.
-
GLIP-T (A), (B) 및 (C)의 Performance 차이를 볼 때, deep fusion 방식은 2 AP, grounding data는 1.8 AP을 향상시킴을 알 수 있다. (저자는 가장 강력한 contributor가 grounding data라고 하던데..)
-
반면에 image-text data의 도입으로 향상된 점은 없었기에, rare class에 관한 분석을 위해 LVIS experiments를 수행했다.
-
-
4.2. Zero-SHot Transfer on LVIS
-
Model의 zero-shot performance 검증을 위해 LVIS Dataset 중에서 diverse하고 rare한 object를 사용하여 평가했다. LVIS Dataset 중, 5,000 장의 이미지를 포함한 MiniVal과 full-validation set을 사용하여 검증하였다.
-
Zero-shot evaluation으로도 GLIP-T는 MDETR과 유사한 수준의 성능을, GLIP-0L은 Supervised-RPS를 크게 압도하는 성능을 보여주었다.
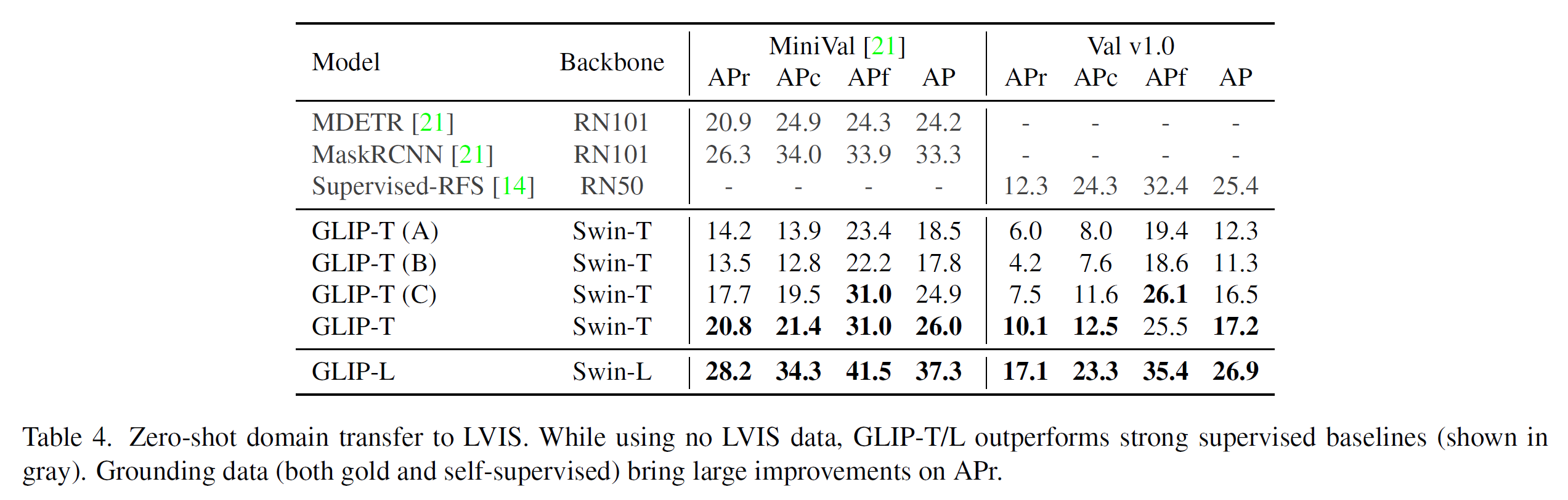
- 결과적으로, Gold-grounding data는 4.2 AP, image-text data는 3.1 AP를 증가시켜서, semantically rich grounding data가 rare object recognition에 중요한 영향을 미치는 것을 확인했다.
-
-
4.3. Phrase Grounding on Flickr30K Entities
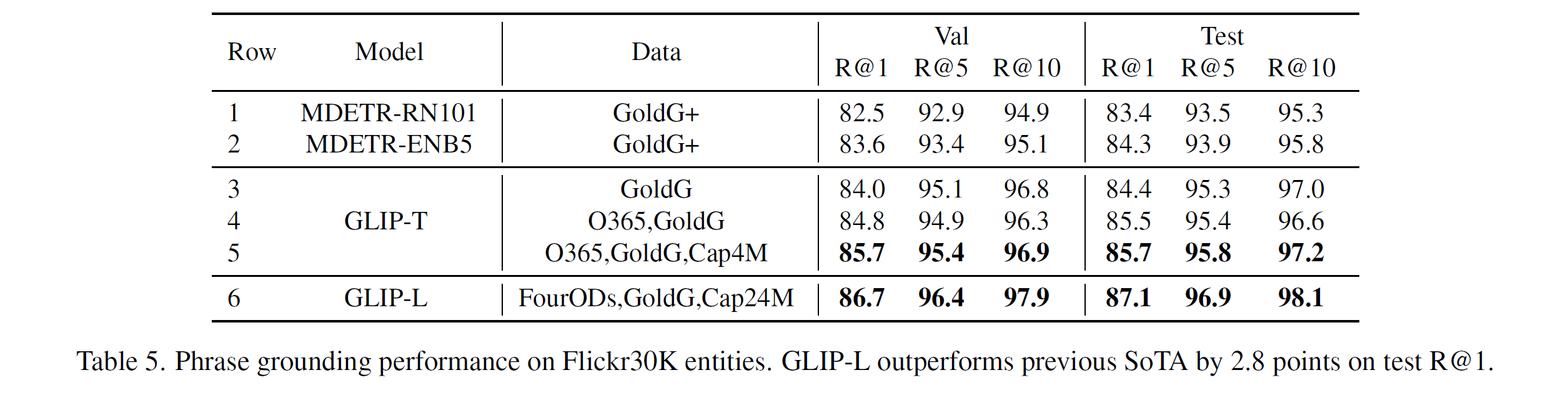
- Model의 ground entities를 평가하기 위해, Flickr30K (Image-text data with human annotations) datasets을 이용하여 MDETR과 같이 Pre-training을 하고 (??) 평가를 진행했다.
-
GLIP-T (With gold-grounding data)는 MDETR(GoldG+)과 유사한 결과를 냈다. 또한 detection data를 추가하는 것은 image 및 text correlated task 사이의 시너지를 향상시켜준다는 것을 결과로부터 다시 한 번 확인할 수 있었다.
-
GLIP-L은 SOTA보다 2.8 AP 높은 87.1 Recall을 달성했다.
-
4.4. Analysis
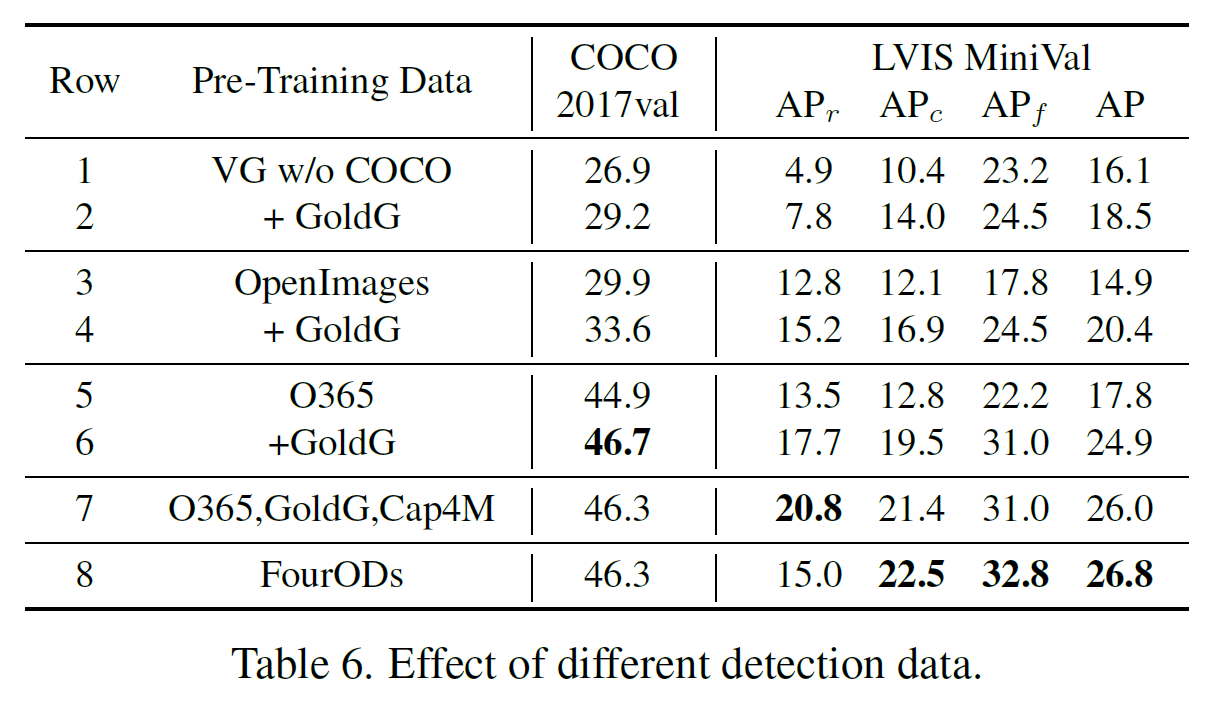
- 이번 section에서는 다른 데이터 셋에 관해 GLIP-T의 Performance를 ablation study 형식으로 파악해보았다.
-
기본적으로는 detection dataset으로부터 bootstrap하는 방식으로 데이터를 만들었다. 이 때, detection dataset과 grounding data가 기존 pair가 아니더라도 효과가 좋을 수 있을까? 하는 의문점이 드는데, 3가지의 다른 데아터 셋 (bootstrap 방식으로 추출?)을 훈련시켰을 때는, 여전히 grounding data의 포함된 것이 performance가 더 좋았다.
-
두 번째로, 일반적으로는 image와 categories를 늘리는 방식으로 dataset을 scaling-up 하는데, 이 방식에 비해서 grounding data를 scaling-up 하는 것이 얼마나 효과가 좋을까? 하는 의문점이다.
-
결과적으로는, image와 categories만을 늘린 dataset으로 GLIP-T를 훈련시키는 것은 performance 증가가 없었고, gold-grounding data 및 image-text를 늘리는 것은 performance가 크게 향상됨을 확인했다.
5. Object detection in the wild
-
GLIP가 Real-world problem에 얼마나 잘 적용될 수 있을지 알기위해서, 13개의 dataset (Target size, ratio 등이 조금씩 다른 dataset들)을 조합해서 ‘Object detection in the wild’ 환경을 만들고 test 해보았다. (Detail한 내용은 Appendix 참조)
-
결과적으로 두 가지 점을 통해서 GLIP의 Transfer performance가 뛰어나다는 것을 확인했다.
-
Dataset의 fit한 data를 사용하지 않고도 baseline과 비슷한 performance를 보였다.
-
새로운 task에 적용시에, 모델은 그대로 두고 입력 text만 바꾸는 것으로도 좋은 performance를 보였다는 것을 볼 때, new domain transfer strategies를 enable하게 만들었다.
-
-
5.1. Data Efficiency
-
실험은 task-specific한 data를 zero-shot (no data provide)부터 X-shot (Provide at least X examples per category)까지 변화시키면서 측정했다.
-
데이터 셋은 training data 중 category name을 pre-specified name으로 변형하되, hyperparameter는 고정시켜놓고 fine-tuning하는 식으로 진행하였다.
-
figure 3은 SOTA Model인 DyHead-T (pre-trained with Object 365)와 비교한 결과치를 나타낸다.

- 또한 각 데이터 셋에 대한 결과는 figure 4 및 appendix에서 나타난다.

-
-
5.2. One Model for All Tasks
-
Model이 커질수록 deployment에 관련된 주제는 부각되어 왔고, 따라서 한 모델이 얼마나 task-specific한 parameters 없이도 generalization이 잘 되는지가 중요하게 다뤄져왔다. 따라서 본 section에서는, GLIP를 deployment efficiency metric을 통해 평가했다.
-
5.2.1. Manual prompt tuning
-
GLIP가 Language input에 따라서 큰 영향을 받는 만큼, 사용자가 이미지를 표현하는 어구를 자세하게 표현할 수록 GLIP의 Transfer 성능을 좋게 만들 수 있다.
-
예를 들어, figure 5를 보면 input으로 object가 flat하고 round하다는 정보를 추가적으로 전달하는 것 만으로도, detection rate이 향상되었음를 확인할 수 있다. 이건 GPT-3과 매우 유사하게, 추가적인 annotated data나 model re-training 없이도 원하는 task를 수행 가능하다는 것을 뜻한다.

-
-
5.2.2. Prompt tuning
-
우리는 easy한 deployment를 위해서 최소한의 parameter만 tuning하는 prompt tuning 방식을 사용한다.
-
Detection 관련 연구 중 하나 [56]에서는 box regression 및 classification head만 training 시키는’linear probing’의 효과를 주장했고, GLIP에서도 region 및 prompt embedding 사이의 box-head 및 projection layer를 fine-tuning하는 방식으로 ‘Linear probing’은 적용될 수 있다.
-
GLIP에서는 ‘Linear probing’을 위해서 language backbone을 사용해서 prompt embeddings를 얻고, 해당 prompt embeddings를 fine-tuning 하는 방식으로 ‘Linear probing’을 수행했다. (즉, language model의 input으로 들어가는 prompt만을 task-specific하게 수정해서 GLIP를 훈련시킴으로써 Task-specific한 network를 쉽게 훈련시킬 수 있다는 의미로 보여진다.)

-
Figure 6은 GLIP의 각 모델들과 Dynamic head model을 각 fine-tuning 및 full-tuning method에 따라 학습시킨 결과를 의미한다.
-
GLIP-T (A) Model은 deep fusion 방식을 사용하지 않았기 때문에 prompt-tuning 및 linear tuning 시 비슷한 결과를 도출하였다. 반면에 GLIP-T 및 GLIP-L은 grounding model을 건드리지 않고, prompt-tuning만 가지고도 full-tuning에 가까운 결과를 얻었다.
-
흥미롭게도, model과 data의 size가 커지면 커질수록, prompt-tuning 및 full-model tuning 사이의 performance 차는 줄어들었다. (GLIP-T, GLIP-L 비교 시).
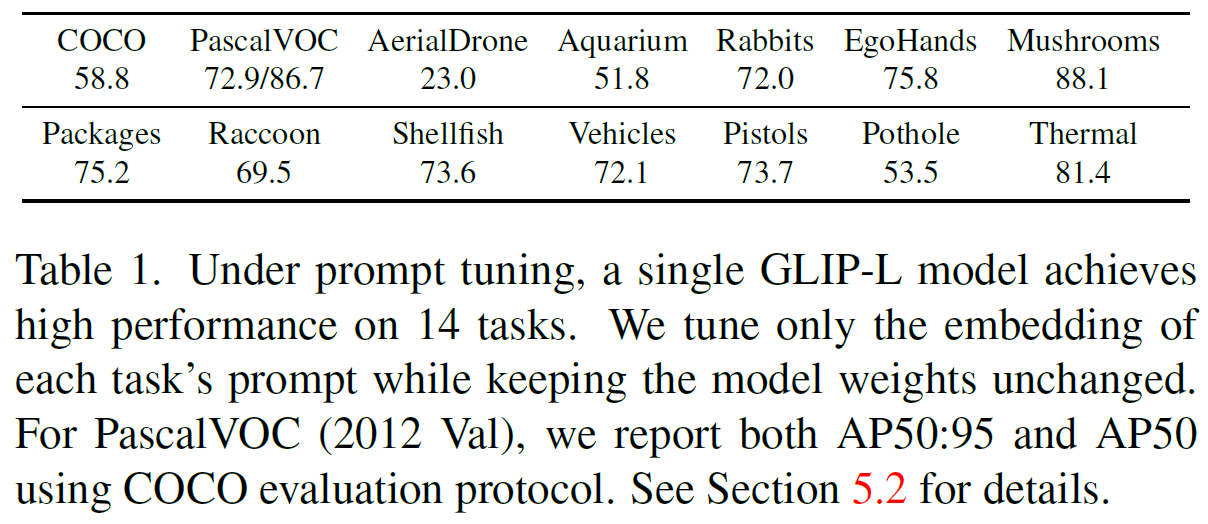
- Table1에서는 GLIP-L이 prompt-tuning (With COCO)시, 14개의 dataset에서 높은 성능이 도출가능함을 보여준다.
-
-
6. Conclusion
- GLIP는 object detection - phrase grounding을 통합한 네트워크로서, 여러 가지 조건의 fine-tuning 만으로 13개의 Object detection downstream task에서 좋은 결과를 보여주었다.

댓글남기기