[Pattern recognition] Feasibility of Learning
시작하기전에
본 포스팅은 패턴인식 수업 수강 후 Feasibility of Learning에 대한 기본적인 지식들에 대해 복습할 기회 제공을 위해 개인적으로 만든 복습 문제 및 정답 포스팅입니다.
Questions
-
What is the hoeffding-Enequality?
-
What is the learning?
-
What is the in-sample error?
-
What is the out-of-sample error?
-
What is the Union-Bound?
-
Describe the uniform version of hoessding-Eneqaulity.
-
What is the ultimate goal of the machine learning?
-
How we can do Feasibility of Learning well?
-
What is the sample complexity?
-
What is the hypothesis complexity?
-
What is the condition of hypothesis when $E_{in} ~= E_{out} $ ?
-
What is the condition of hypothesis when $E_{in} ~= 0$ ?
-
What is the compact between 11, 12 ?
-
What is the point-wise error?
-
What is the overall error?
-
How we measure the error?
-
What is the difference between the interpolation and regression?
-
What is the P(y x) ? -
What is the $P(x)$ ?
- What is the PAC ?
Answer
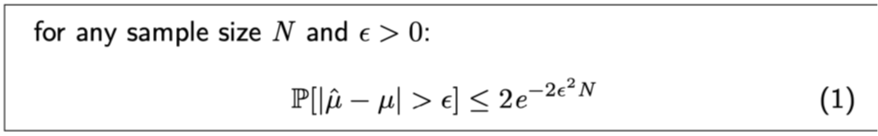
-
The estimation of Target value for using prediction.
-
$u, u^^$ is the prediction value and target value.
-
The $P$ is probility of bad event.
-
N is the size of dataset.
-
If N is high enough, $u, u^^$ will be similar than that N was small.
-
And if $\epsilon$ is high, the approximation of $u$ is better. But we need more sample.
-
-
The process finding optimal hypothesis in the hypothesis set.
-
The probability that the result deduced from the hypothesis is wrong in the data for which I know the correct answer.
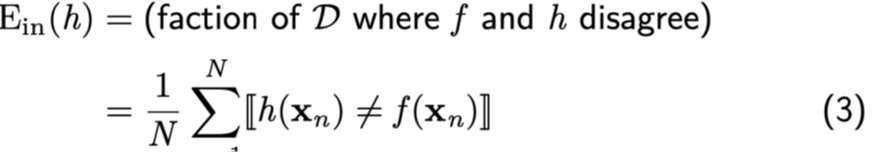
-
Probability that the inferred result from a population I do not know is not the same as the target function.
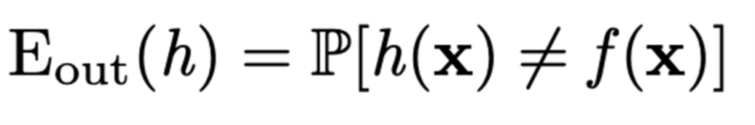
-
$P[A \cup B] <= P[A] + P[B]$
-
The version of multi hypothesises. Is has meaning when the hypothesis set is finite.
- $P[E_{in}(g)-E_{out}(g)>\epsilon ]<= 2Me^(-2*\epsilon^2 N)$
-
Minimize the $E_{out}(g) ~= 0$
- But it can not be real because our model has dependency in dataset.
-
Two condition.
-
$E_{out}(g) ~= E_{in}(g)$
-
$E_{in}$ must be small enough.
-
-
The number of training example.
-
The number of Hypothesises.
-
The hypothesis must be less complex. You can figure out with 6.
-
The hypothesis must be complex. Although there is a danger of overfitting, a complexity is required for reducing error.
-
Approximation-Generalization trade-off.
-
The error of each sample.
-
The average of point-wise error.
-
False accept, False reject.
-
Interpolation means a method that satisfies all samples. Machine learning x.
- Target function exactly satisfies y_n. That is, E_in=0.
- Regression does not satisfy all samples. Machine learning o
-
The target distribution cared for noise.
-
Input distribution.
-
Probably approximately correct.

댓글남기기